Automating releases on GitLab¶
In this tutorial you'll create multiple automated releases for a GitLab project. You'll use the release-it tool with our GitLab pipeline template to configure a release pipeline and trigger automated released using one of two available workflows.
Prerequisites¶
- The GitLab project that you wish to use must have been deployed via the gitlab-project-factory Terraform configuration and the code should've been created via the WebApp Boilerplate.
- A product-specific Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) runner must have been deployed via the gitlab-runner-infrastructure Terraform configuration.
- You must have followed the steps in How to enable automated GitLab
releases to enable the release
pipeline and create a
.release-it.jsonconfig file in your repository.
Default workflow¶
The default workflow for the release-it.yml GitLab template is based on the
Conventional Commit
specification, as recommended in the Git
Commits section of this guidebook. Each time
commits are merged to the default branch the release job analyses each new
commit message and determines what the next version of the code should be.
The following steps show you how to use this workflow to create a new minor release for your project.
-
Checkout a new branch for your feature.
git checkout -b my-new-feature -
Make the required changes to your source code and create a git commit using the Conventional Commit
featprefix in the commit message.git add --all git commit -m "feat: my awesome feature" -
Push the new branch to the GitLab remote.
git push -u origin my-new-feature -
In the GitLab UI, open a merge request to merge the
my-new-featurebranch into the default branch. -
Once the merge request has been approved and merged you'll see a
releasejob in the triggered pipeline. This job will invoke therelease-itcommand to perform the tasks configured in your project's.release-it.jsonconfig file. If you used the example.release-it.jsonfile from the Enable automated GitLab releases how-to, the following tasks will be performed.- Calculate the next version of your project based on the commit messages since the previous git tag.
- Generate the required updates to the
CHANGELOG.mdandpyproject.tomlfiles and commit them back to the default branch. - Push a new git tag to the repository for the new version.
- Create a GitLab Release corresponding to the new git tag and containing a copy of the generated changelog notes.
Alternate workflow¶
The release-it.yml GitLab template has an alternate
workflow mode
which queues unreleased changes in a draft release merge request.
The following steps show you how to use this workflow to create a new minor release for your project.
-
Checkout a new branch for your feature.
git checkout -b my-new-feature1 -
Make the required changes to your source code and create a git commit using the Conventional Commit
featprefix in the commit message.git add --all git commit -m "feat: my awesome feature" -
Push the new branch to the GitLab remote.
git push -u origin my-new-feature1 -
In the GitLab UI, open a merge request to merge the
my-new-feature1branch into the default branch. -
Once the merge request has been approved and merged you'll see an
update-release-merge-requestjob in the triggered pipeline. This job will create/update a draft merge request containing the proposed changes to theCHANGELOG.mdandpyproject.tomlfiles for the next version of your code. The following is an example of this merge request.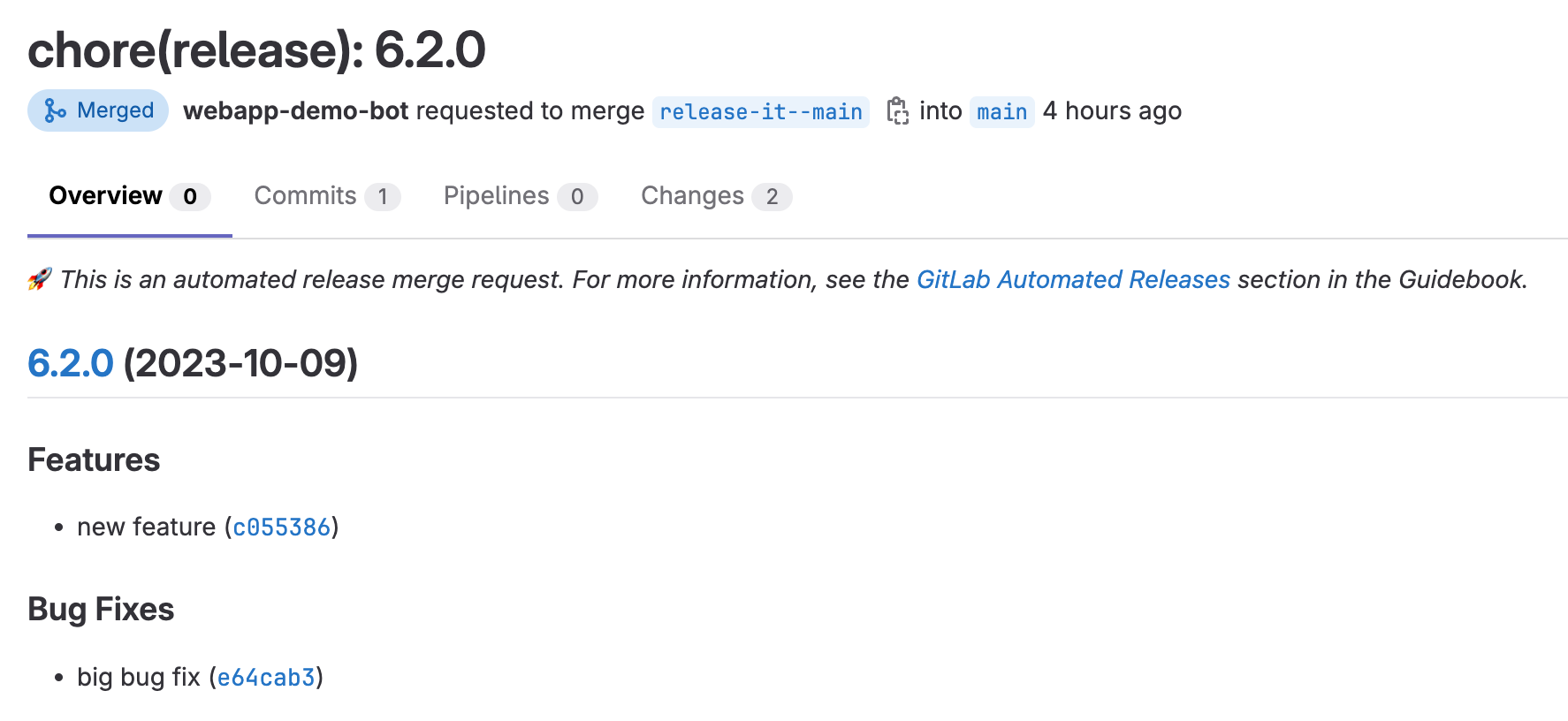
-
Once you're ready to release this version simply approve and merge the release merge request. Merging this MR will trigger a pipeline containing the
releasejob which will perform the git tag and create the corresponding GitLab Release.
Creating a hotfix for a previously released version¶
Creating a patch for a previously released version can also be automated using
either of the two workflows above. The main requirement is that you create a
branch named with the prefix release/fix-. For example, assuming you had previously
released versions 1.0.0 and 2.0.0 of your project but you now need to fix a
bug in the original version 1.0.0 code you could do the following.
-
Checkout a new hotfix branch from the
1.0.0tag.Note
Using an
xin the branch name is not mandatory but can be useful as you may need to fix other bugs in the1.0.0version of your code in the future. However, the process would work the same if you wanted to name your branchrelease/fix-1.0.1instead.git checkout -b release/fix-1.0.x 1.0.0 -
Push the hotfix branch to the remote repository.
git push -u origin release/fix-1.0.x -
Create a new branch to hold your bug fix commit.
git checkout -b fix-that-annoying-bug -
Make the required changes to your source code and create a git commit using the Conventional Commit
fixprefix in the commit message to denote that this is a bug fix.git add --all git commit -m "fix: fix that annoying bug" -
Push the new branch to the GitLab remote.
git push -u origin fix-that-annoying-big -
In the GitLab UI, open a merge request to merge the
fix-that-annoying-bugbranch into therelease/fix-1.0.xhotfix branch. -
Once the merge request has been approved and merged you'll see either the
releasejob or theupdate-release-merge-requestjob in the triggered pipeline depending on which of the above workflows you are using.If you're using the default workflow, the
releasejob will perform the full1.0.1release at this stage. If you're using the alternate workflow, the draft merge request will be waiting to be merged into therelease/fix-1.0.xbranch when you're ready to release the1.0.1version.
See also¶
For more information on how this process works see the GitLab release automation page in the Explanations section.